Periodic Table: 105 Common Questions Answered for the year 2024
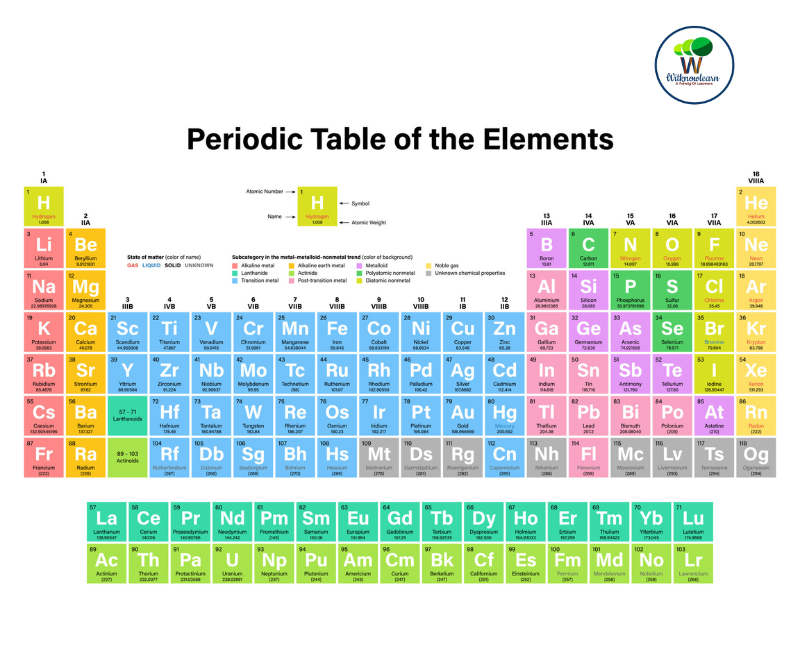
Introduction to the Periodic Table: The Building Blocks of Matter
The Periodic Table of Elements is more than just a scientific icon; it's a vast grid that holds the secrets of the universe! An understanding of the Periodic Table allows us to comprehend the building blocks of the world around us, from the air we breathe to the core of distant stars.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. Elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number, which corresponds to the number of protons in an atom's atomic nucleus.
The table has rows called periods and columns called groups. The groups contain elements with similar properties, due to the similar outer shell electron configuration.
The periodic table is divided into several blocks:
S-Block: This includes Group 1 (alkali metals) and Group 2 (alkaline earth metals) plus hydrogen and helium.
P-Block: This includes Groups 13 to 18, containing a wide range of metallic, semi-metallic, and non-metallic elements.
D-Block: This includes transition metals, which are Groups 3 to 12.
F-Block: This includes the Lanthanides and the Actinides series. These elements are often listed separately at the bottom of the Periodic Table to keep the table compact.
the periodic table consists of 118 confirmed elements, from element 1 (hydrogen) to element 118 (oganesson). Some of these elements are naturally occurring, while others have only been created synthetically in laboratories.
The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, allowing scientists to understand the relationships between various elements, predict the properties of new, yet-to-be-discovered or synthesized elements, and interpret or predict how different elements will react with each other.
periodic table period and group
In the periodic table, a period refers to a horizontal row, while a group refers to a vertical column.
Periods: The periodic table consists of seven periods, numbered from 1 to 7. As you move from left to right across a period, each element has one more proton and electron than the previous element. This increment changes the properties of the elements. Also, as you move from left to right, the elements become less metallic. The first element of a period is always an extremely active metal (like sodium or potassium), while the last element of a period is always an inactive noble gas (like neon or argon).
Periodic table group
Groups: The periodic table consists of 18 groups, numbered from 1 to 18 (in some versions, the groups in the middle are labeled with Roman numerals and the letters A and B). Elements in the same group have similar chemical and physical properties. This is because they have the same number of valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom that determine its chemical reactivity. For example, all elements in Group 1 (also known as alkali metals) have one valence electron and are highly reactive, while elements in Group 18 (also known as noble gases) have a full set of valence electrons and are very stable and unreactive.
The transition metals, which are the elements in the middle of the table, are often considered as a separate series rather than belonging to groups 3-12 because they have similar properties to each other, but not to the rest of the groups.
In addition to these, the elements can be divided into blocks (s, p, d, f) based on their electron configuration. Each block includes elements from certain groups: s-block includes groups 1 and 2, p-block includes groups 13-18, d-block consists of transition metals (groups 3-12), and f-block includes the inner transition metals (lanthanides and actinides).
List of Periodic Table Elements in the year 2024
All 118 elements of the Modern Periodic Tabe are listed below.
Click here to download periodic table high resolution image
Click here to download Periodic table flashcards
105 Periodic table questions and their answers asked by students
*Note some of the questions may have the same meaning and answers
Who discovered the modern periodic table?
The modern periodic table was largely developed by Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, in 1869. Mendeleev's table organized elements by atomic weight, and he even left blank spaces in his table where he predicted unknown elements would fit, many of which were discovered later.
Who arranged the periodic table?
Initially, Dmitri Mendeleev arranged the periodic table. However, the modern arrangement is based on the atomic number (number of protons), not atomic weight. This adjustment was made following the work of Henry Moseley in 1913.
Who periodic table?
it's widely used by chemists, physicists, biologists, engineers, and science students worldwide. It's a fundamental tool in science education and research.
Who invented the periodic table?
The periodic table was invented by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. However, it's worth noting that other scientists, like Lothar Meyer, were also working on similar ideas around the same time.
Who created the periodic table and how is it organised or arranged?
Dmitri Mendeleev created the periodic table. In the modern version, the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The table is laid out in rows, or periods, which correspond to the number of energy levels or shells in an atom. The columns, or groups, contain elements with the same number of electrons in their outer shell and therefore have similar chemical properties.
Who used the periodic table?
The periodic table is used by anyone studying or working in fields that involve chemistry. This includes chemists, materials scientists, physicists, biologists, pharmacists, and students in various scientific disciplines. It's used to understand and predict how different elements will interact with each other.
Who does the periodic table work?
it works by organizing elements based on their atomic structure and chemical properties. The arrangement allows scientists to understand the relationships between different elements, predict how they will interact, and even predict the properties of elements that hadn't been discovered at the time of its creation.
How is the periodic table arranged?
The periodic table is arranged based on atomic number (the number of protons in an atom's nucleus). It has rows (periods) that correspond to the number of energy levels in an atom, and columns (groups) that contain elements with the same number of electrons in their outer shell, which results in them having similar chemical properties.
How does the periodic table work?
The periodic table works by organizing elements based on their atomic structure and chemical properties. The arrangement allows scientists to understand the relationships between different elements, predict how they will interact, and even predict the properties of elements that hadn't been discovered at the time of its creation.
How many periodic tables are there?
There is only one periodic table, but there are different representations or formats of it, such as the long form, short form, or circular versions. However, they all contain the same fundamental information about the elements.
How did the periodic table develop?
The development of the periodic table was a gradual process that involved many scientists. Dmitri Mendeleev is credited with its creation in 1869, but many before him tried to categorize elements. Mendeleev's original table was based on atomic weight, but it later shifted to atomic number after Henry Moseley's work in 1913.
How many elements were in the periodic table in 2021, 2022, and 2024
there were 118 confirmed elements on the periodic table in the year 2024
How is the periodic table organized?
The periodic table is organized in rows and columns based on atomic number and electron configuration. Elements in the same column (group) have similar properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shell.
How much of the periodic table is elements?
The entire periodic table is made up of elements. Each square in the table represents a unique chemical element.
How much of the periodic table is metals?
Most of the elements on the periodic table are metals, specifically around 75%.
How is the periodic table classified?
The periodic table is classified into several sections: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block. It also divides elements into categories based on their properties, such as alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, post-transition metals, metalloids, nonmetals, halogens, and noble gases.
How was the periodic table discovered?
The periodic table was developed over time, but Dmitri Mendeleev is credited with its creation in 1869. He was able to arrange the elements known at that time in a way that showcased their periodic properties, leaving gaps for elements yet to be discovered.
How often is the periodic table updated?
The periodic table is updated whenever new elements are discovered and their discoveries are confirmed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). This is not on a set schedule and can vary widely.
How was the periodic table made?
The periodic table was made by arranging the elements in order of increasing atomic weight, a method originally proposed by Dmitri Mendeleev. However, the modern periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number, a change that was made after the discovery of isotopes and the work of Henry Moseley.
How many periodic tables are in chemistry?
There is one fundamental periodic table used in chemistry, but it can be represented in various ways, such as the long form or short form.
How many elements are in the periodic table of 2024
There were 118 confirmed elements on the periodic table.
How many families are in the periodic table?
There are 18 vertical groups or "families" in the periodic table. These families include alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, post-transition metals, metalloids, nonmetals, halogens, noble gases, and the f-block elements.
How many elements are in liquid form at room temperature?
only two elements are liquid at room temperature: bromine (Br) and mercury (Hg).
How much does a periodic table cost?
The cost of a physical copy of the periodic table can vary widely depending on the size, material, and level of detail. You can typically find posters or laminated copies for educational use between $10 and $20. However, digital versions are often available for free online.
How many times has the periodic table changed?
The periodic table has changed many times since Dmitri Mendeleev first proposed it in 1869. It has been updated to accommodate new elements and to reflect better understandings of atomic structure and quantum mechanics. There were 63 known elements when Mendeleev first created the periodic table, and as of January 2024, there are 118 confirmed elements.
Why is the periodic table important?
The periodic table is important because it organizes all known chemical elements in a systematic and logical way. It allows scientists to understand patterns and trends among elements, predict the properties of elements, and understand how different elements will interact with each other.
Why is the periodic table called the periodic table?
The periodic table is so named because it arranges the elements in a way that periodic trends, or repeating patterns of behavior, can be observed among the elemental properties.
Why is the periodic table important in chemistry?
The periodic table is critical in chemistry as it provides a comprehensive overview of the elements and their properties, facilitating the prediction of how they will interact and combine to form compounds. It aids in understanding and interpreting chemical behavior.
Why was the periodic table made?
The periodic table was made to categorize, organize, and compare all of the chemical elements, based on their properties and behaviors. It was intended to bring order to the then-growing list of known elements.
Why was the periodic table developed?
The periodic table was developed to provide a logical system for organizing the known elements. Prior to its development, scientists struggled to understand the relationships between the various elements.
Why is the periodic table arranged by atomic number?
The periodic table is arranged by atomic number because it corresponds to the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, which is a fundamental property of an element. This arrangement reflects the electron configuration of the atoms, which in turn determines their chemical behavior.
Why was the periodic table removed from the syllabus?
and Why was the periodic table removed in India? I'm sorry, but as of my last training data in September 2021, I have no information regarding the periodic table being removed from the syllabus in any specific region, including India. Educational policies can change, and for the most accurate information, it would be best to consult the relevant educational authorities or official documentation.
Why was the periodic table dropped?
Without specific context, it's challenging to address this question. The periodic table is a fundamental tool in science and is widely taught and used. If it has been dropped from a specific context (like a course or curriculum), the reasons could vary widely.
Why is the periodic table needed?
The periodic table is needed because it provides a system for organizing and understanding elements and their properties. It helps scientists predict how elements will interact, aids in the identification of unknown elements, and assists in the design of new materials.
Why is the periodic table arranged in the way it is?
The periodic table is arranged based on atomic number and electron configuration, which reflects the quantum mechanical nature of the atoms. This arrangement groups elements with similar properties together, and the properties of the elements show periodic (repeating) trends as you move through the table.
Why was the periodic table invented?
The periodic table was invented to organize and classify the elements based on their properties. It helped scientists understand the relationships between various elements, predict the properties of new elements, and study existing ones more effectively.
Why were early periodic tables ordered by atomic mass?
Early periodic tables, such as the one by Dmitri Mendeleev, were ordered by atomic mass because, at the time, the concept of atomic number (number of protons in an atom's nucleus) was not yet understood.
Mendeleev noticed that when elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, similar properties recurred at regular intervals - or periods. This led him to the idea of the "periodic" table. Despite some anomalies where elements seemed to be in the wrong order if arranged by atomic mass, Mendeleev even had the foresight to leave gaps in his table for undiscovered elements.
The modern periodic table is arranged by atomic number, rather than atomic mass, thanks to the work of Henry Moseley in 1913. His work on X-ray spectra of the elements showed that a better ordering principle was atomic number, not atomic mass. This change resolved the previous inconsistencies and provided a solid basis for the modern periodic table.
How many periodic tables are there?
There is only one periodic table of elements. However, it can be presented in different formats or visual styles. All representations, though, have the same basic information and structure.
How many periodic table elements are there?
As of my knowledge cutoff in September 2023, there are 118 confirmed elements on the periodic table.
How many periodic table groups are there?
There are 18 vertical columns or groups on the periodic table.
Are periodic table symbols allowed in Scrabble?
In standard Scrabble rules, abbreviations and symbols aren't allowed, so the two-letter symbols for elements would not be valid. However, some people might play with their own house rules that allow for such usage.
What periodic table element am I?
As an AI, I don't have a physical form, so I can't be represented by an element on the periodic table.
What does each period in the periodic table correspond to?
Each period in the periodic table corresponds to the highest energy electron's principal quantum number, which effectively indicates the energy level of an atom's electron shell.
What cannot be found on the periodic table?
The periodic table includes all known chemical elements. It doesn't include mixtures, compounds, subatomic particles (like protons, neutrons, or electrons), or physical objects (like rocks or molecules).
What periodic table group is oxygen in?
Oxygen is in Group 16, also known as the chalcogens.
What periodic table elements are found in a chassis?
A chassis, like that of a car, is typically made of metal or alloy. Common elements could include iron (Fe) in steel, or aluminium (Al). Carbon (C) may also be present in steel or in carbon fiber composites.
What periodic table group is aluminium in?
Aluminium is in Group 13, often referred to as the boron group.
What does the periodic table tell us?
The periodic table provides information about each known chemical element, including its atomic number (number of protons), symbol, name, and atomic weight. It also organizes elements by their chemical properties and electron configurations, allowing us to see trends and make predictions about elemental properties and reactions.
What periodic table group is uranium in?
Uranium is in the actinides series, which is part of the f-block of the periodic table.
What periodic table group is calcium in?
Calcium is in Group 2, the alkaline earth metals.
What periodic table group is silicon in?
Silicon is in Group 14, sometimes known as the carbon group or tetrels.
What periodic table group is titanium in?
Titanium is in Group 4, part of the transition metals.
What periodic table group is nitrogen in?
Nitrogen is in Group 15, also known as the pnictogens or nitrogen group.
Does the periodic table have all the elements?
Yes, the periodic table includes all known chemical elements. As of my last training data in September 2021, this includes 118 confirmed elements. If new elements are discovered, they are added to the periodic table.
Does the term 'periodic table' need to be capitalized?
The term 'periodic table' is typically not capitalized in general use unless it starts a sentence. However, specific versions or representations of the table (like the "Mendeleev's Periodic Table") might be capitalized as per English grammar rules.
What does 'periodic table' mean?
The term "periodic table" refers to a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. Elements are ordered in rows, or periods, in which elements display similar behavior to elements in the same column, or group
Do you need to learn the periodic table?
The need to learn the periodic table depends on what you are studying or your field of work. It's fundamental in fields like chemistry, physics, and certain areas of biology and geology. Even if not memorizing the entire table, understanding its structure and how to read it is often part of science education.
Where on the periodic table is hydrogen?
Hydrogen is the first element on the periodic table. It is located at the top left corner, in Group 1.
Where on the periodic table are the transition metals?
The transition metals are located in the middle of the periodic table, specifically in Groups 3-12.
Where on the periodic table are the radioactive elements?
The radioactive elements are primarily located at the bottom of the periodic table, in the actinide and lanthanide series. However, some other elements, like uranium and thorium, are also radioactive.
Where is the periodic table staircase?
The "staircase" on the periodic table is a step-like line that separates the metals from the nonmetals. It starts under boron (Group 13, Period 2) and steps down through silicon, arsenic, tellurium, and astatine.
Where are the metalloids on the periodic table?
Metalloids are located along the staircase line on the periodic table. These include boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium, and polonium.
Where in the periodic table are the noble gases?
The noble gases are located in Group 18, the far right column of the periodic table.
Where on the periodic table is the most electronegative element?
The most electronegative element, fluorine, is located in Group 17, Period 2 of the periodic table.
Where on the periodic table are the valence electrons?
The group number (for Groups 1-18) of the periodic table corresponds to the number of valence electrons for the elements in those groups.
Where on the periodic table are the metalloids located?
The metalloids are located along the staircase line on the periodic table. These include boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium, and polonium.
Where on the periodic table are alkali metals?
Alkali metals are located in Group 1 of the periodic table, but do not include hydrogen.
Where on the periodic table are the most reactive metals?
The most reactive metals, the alkali metals, are located in Group 1 of the periodic table. Of these, francium is theoretically the most reactive, although its instability and rarity make cesium practically the most reactive of the alkali metals.
Where on the periodic table are the transition metals located?
The transition metals are located in Groups 3-12 of the periodic table. They occupy the central block of the table.
Which periodic table family is the least reactive?
The least reactive family on the periodic table is the noble gases (Group 18). They have a full set of electrons in their outer shell, making them stable and not prone to reactions.
Which periodic table family is the most reactive?
In general, the alkali metals (Group 1) and the halogens (Group 17) are the most reactive families on the periodic table. Alkali metals are extremely reactive metals and halogens are very reactive non-metals.
Which periodic table has a cylindrical shape?
The periodic table is traditionally presented as a flat, tabular arrangement, but some representations show it as a cylindrical or spiral shape to emphasize the continuity of periodic properties. One example of such an alternative representation is the Alexander Arrangement of Elements.
Which periodic table do we use?
Today, we use the long-form of the periodic table, also known as the 18-column form, which was first described by Glenn T. Seaborg in 1945 and expanded over time as new elements have been discovered.
Which periodic table is used today?
The periodic table used today is based on the one devised and published by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, with additions and modifications. It's an 18-column chart known as the long-form of the periodic table.
Which periodic table elements are metals?
The majority of the elements in the periodic table are metals. These include alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides, post-transition metals, and some metalloids. They are located on the left and center of the periodic table.
Which periodic table elements are radioactive?
The radioactive elements are primarily located in the actinide series of the periodic table, which includes elements like uranium and plutonium. However, other elements like technetium (in the transition metals) and all the elements beyond bismuth (atomic number 83) are also radioactive.
Which periodic table is best?
The "best" periodic table depends on the purpose for which it is being used. The most commonly used format is the long form or 18-column table because it clearly shows the relationships and trends among the elements. However, other forms may be more useful for specific applications.
Which periodic table groups contain only metals?
Groups 1 (alkali metals, excluding hydrogen), 2 (alkaline earth metals), and 3-12 (transition metals) contain only metals. The lanthanide and actinide series are also all metals.
Is potassium in the periodic table?
Yes, potassium is an element and it is in the periodic table. Its symbol is K and it is located in Group 1, Period 4.
Is methane in the periodic table?
No, methane is not in the periodic table because it is a compound, not an element. The periodic table includes only pure elements. Methane is a compound composed of carbon and hydrogen.
Is the periodic table organized?
Yes, the periodic table is organized based on atomic number (number of protons in an atom's nucleus) and chemical properties. Elements are arranged in rows (periods) and columns (groups) to highlight trends in element properties.
Is the periodic table of elements a metal?
No, the periodic table of elements is not a metal. It is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements. However, many of the elements in the periodic table are metals.
Is the periodic table atoms?
The periodic table represents all known atoms, or chemical elements. Each element in the table represents a type of atom.
Is the periodic table on the MCAT?
Yes, the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) does involve chemistry and biology questions that require knowledge of the periodic table.
Is the periodic table atomic mass?
The periodic table includes the atomic masses of all elements, but it is not an atomic mass itself. It is an arrangement of all known elements based on atomic number and chemical properties.
Is the periodic table easy?
The ease of understanding the periodic table can vary from person to person. With basic chemistry knowledge, one can understand the organization and various properties of elements presented in the table. However, fully grasping the complexity of the information it holds might require more advanced study.
Is the periodic table in grams?
No, the periodic table is not in grams. However, the atomic mass unit listed for each element on the table is roughly equivalent to the mass of one atom of that element expressed in grams divided by Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10^23).
Is the periodic table physics?
The periodic table is a tool primarily used in chemistry to organize elements based on their atomic structure and properties. However, because atomic structure and properties are also relevant to physics, the periodic table is useful in this field as well.
Is there a limit to the periodic table?
In theory, there may be a limit to the periodic table as elements with higher and higher atomic numbers tend to become more unstable and have shorter and shorter half-lives. However, as of my knowledge cutoff, it is not definitively known where that limit might be.
Is the periodic table important?
Yes, the periodic table is incredibly important in chemistry and other sciences as it organizes elements based on their atomic structure and properties, allowing scientists to understand and predict how different elements will interact.
Is the periodic table complete?
The periodic table is complete in the sense that it includes all known elements as of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021. However, scientists are continually working to synthesize new elements, so new elements may be added in the future.
Will the periodic table ever be completed?
It's hard to say for certain. The periodic table is complete for all currently known elements, but new elements could potentially be discovered or synthesized. However, elements with higher atomic numbers tend to be unstable and short-lived, which may limit the potential for new additions.
Can I learn the periodic table?
Yes, anyone can learn the periodic table. There are many resources available, including textbooks, online tutorials, and mnemonic devices to help remember the order of the elements.
How can I memorize the periodic table?
Memorizing the periodic table can be accomplished through various methods such as flashcards, songs, mnemonic devices, or even mobile apps designed for this purpose. Regular practice and review can help reinforce this knowledge.
Can the periodic table be arranged differently?
Yes, the periodic table can be arranged differently, and there are indeed various versions of the periodic table. However, the standard version is arranged based on atomic number and the properties of the elements, which shows the periodic trends most effectively.
Can we use periodic table in Scrabble?
In Scrabble, you can use the names of chemical elements as they are listed in the dictionary. However, you can't use the symbols of elements as they are not recognized English words.
What are the different blocks in the periodic table?
The periodic table is divided into four blocks:
- The s-block, including groups 1 and 2, and helium. These elements have their last electron in the s orbital.
- The p-block, including groups 13 to 18. These elements have their last electron in the p orbital.
- The d-block, containing transition metals from groups 3 to 12. These elements have their last electron in the d orbital.
- The f-block, comprising the lanthanides and actinides. These elements have their last electron in the f orbital.
What is the periodic law?
The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic pattern in their physical and chemical properties. This pattern repeats after certain intervals, giving the table its 'periodicity'.
How is the atomic radius determined in the periodic table?
Atomic radius generally decreases across a period from left to right and increases down a given group. This is because as you move across a period, electrons are added to the same energy level while the nucleus gains protons, causing an increased positive charge and pulling the electrons closer to the nucleus. As you move down a group, electrons are added to new energy levels that are further from the nucleus, increasing the atomic radius.
What is a period in the periodic table?
A period in the periodic table refers to a horizontal row. Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells, or energy levels. The period number indicates the highest energy level an electron occupies for an element in the ground state.
What is a group in the periodic table?
A group in the periodic table refers to a vertical column. Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties due to the same number of valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
What do the atomic number and symbol represent on the periodic table?
The atomic number, located above the element symbol on the periodic table, represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom for that particular element. The symbol is a one- or two-letter abbreviation of the element's name. The symbol can be derived from the current name of the element, or from its original Latin or Greek name.
Why are there two rows at the bottom of the periodic table?
The two rows at the bottom of the periodic table represent the lanthanides (elements 57-71) and the actinides (elements 89-103). They are placed separately to keep the table compact, but they actually fit into the periodic table's third group.
Why is hydrogen placed separately in the periodic table?
Hydrogen is placed separately in the periodic table because it is unique. While it is part of Group 1 (alkali metals), it's not a metal. Hydrogen is a nonmetal and it exhibits properties of both Group 1 elements and Group 17 elements (halogens).
Are all elements on the periodic table naturally occurring?
No, not all elements on the periodic table are naturally occurring. While the majority of the elements occur naturally, elements with atomic numbers greater than 92 (uranium) are typically synthetic and produced in laboratories or nuclear reactors.
periodic table practice problems for students
- What is the atomic number of neon?
- Which group do the alkali metals belong to?
- How many valence electrons does an atom of oxygen have?
- Which element is located in Period 3, Group 16 of the periodic table?
- Why do elements in the same group often share similar properties?
- What block in the periodic table does argon belong to?
- Which element in Period 2 has the greatest electronegativity?
- Identify the period and group of the element with the electron configuration [Ne] 3s^2 3p^4.
- If an element is located in Group 2, Period 4 of the periodic table, how many valence electrons does it have?
- Are transition metals typically found in the s-block, d-block, p-block, or f-block?
periodic table quiz for students
- What element has the atomic number 1?
- What group are the noble gases in?
- How many periods are in the periodic table?
- What block do the alkali metals belong to?
- What is the symbol for the element with atomic number 79?
- What is the heaviest naturally occurring element on the periodic table?
- Which element is named after the scientist who developed the theory of relativity?
- Which group does the element Fluorine belong to?
- How many valence electrons does an atom of chlorine have?
- What is the common name for elements in Group 17?
- What is the name of the element with the symbol 'K'?
- What block are the lanthanides and actinides part of?
- Which element in Period 3 is a noble gas?
- What are the elements in Group 2 commonly referred to as?
- Which element is considered the 'bridge' element between the metals and nonmetals?
- element i on periodic table.
